Think finance and numbers automatically come into play. And where there are numbers, the risk of human error becomes a certainty. Unless, of course, one has digitally transformed the business where data capture is automated and so is analytics. Some estimates claim that these errors result in more than 25,000 hours of avoidable rework which translates into more than $800,000 in annual costs. However, the winds of automation are making a difference. Today robotic process automation (RPA) is not limited to optical character recognition and automated data feeds across systems. Now, these tools can interact with other applications that include ERP and CRM solutions. Small wonder then that the global RPA market is expected to grow at a CAGR of nearly 40% between 2023 to 2030, from $2.3 billion in 2022.
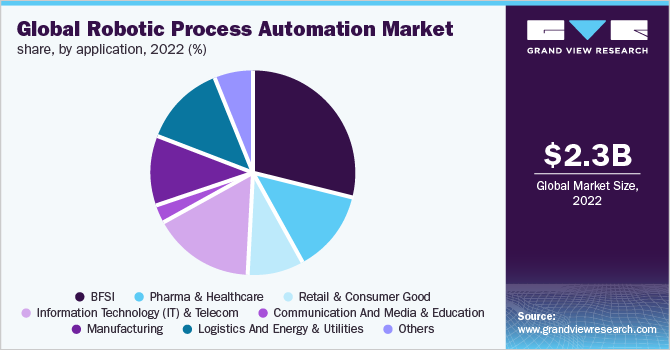
Overall RPA in financial services helps enhance the speed, accuracy, and efficiency of operations through handling large volumes of data more efficiently to reduce errors and save costs. A recent report from Gartner suggests that 80% of companies are clued in to RPA to avail of the cost savings of up to 50%. The current crop of RPA tools can modify data, set off responses, and communicate within a network, while advanced solutions have the ability to review reports and flag issues to maintain the security of the systems they manage. The above graph shows how the BFSI industry is leading the way in the use of RPA tools compared to other industry verticals.
The Shift from Fintech to Finance Departments
For finance departments of an enterprise, RPA largely revolves around the use of customized technologies to automate repetitive tasks such as data entry, account reconciliation, and generation of reports. It supports processes such as accounts payables and receivables management, financial statement preparation, tax reporting, budgeting, and forecasting. With its artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms, RPA also helps in compliance monitoring, risk control, and fraud detection.
When the regular manual work gets handed over to smart RPA technologies, the immediate benefits that come along include faster processing time, enhanced productivity and accuracy, cost savings, improved data management, scalability of operations, and upgrades to the roles and responsibilities of the staff deployed in routine work. However, as the value of RPA increases, it’s important that businesses also get clarity around the best practices that help in its deployment. Some of the key considerations are listed below:
- A steady scale-up – It’s better to start small. So, the initial RPA implementation could be in the nature of a pilot project. This will help to demonstrate the real value of technology to stakeholders and gain the buy-in for bigger processes. Based on the success rate of the pilot, iterations can also be made before scaling the deployment for other domains of the finance department.
- Clarity over goals – While RPA does offer a number of benefits, an organization must have clear objectives for the projects it seeks to innovate before investing in such technologies. The goals must be specific, realistic, measurable and time-bound, given that the success of early pilots often define the way RPA tools get integrated into the rest of the organizational workflow.
- Stakeholder engagement – As mentioned above, stakeholder support across business units is critical for RPA-enablement. Early success with pilot projects helps get easy sign-offs across different units, which are critical to success when an enterprise-level transformation is called for. Stakeholder support to identify pain points and areas where automation will bring improvement is crucial as is their feedback on RPA strategies to ensure that the solutions are constantly reviewed and enhanced.
- Data quality and integrity – Because RPA works on the basis of data for the processes it streamlines, users have to ensure that the information it accesses is accurate, complete, and consistently available. Data quality can be optimized with the regular usage of data cleansing tools.
- Security and compliance – Although automation enables noticeable improvement in efficiency, it can be a source of new risks. When RPA is ready to take over the processes that were earlier handled by humans, the IT team must ensure that the solution is reliable and compliant with applicable industry standards and regulations. Attention to coding practices, software encryption, and access controls is critical for security.
- Tracking and performance metrics – RPA solutions have to be constantly monitored and gauged for their ability to bring the expected results. There should be well-defined KPIs to measure the progress, and reports on the success of automation for different projects should be delivered to the concerned stakeholders.
What Does the Future Hold for RPA?
A recent report by McKinsey notes that the growing use of technology has allowed leaders in the finance department to spend 19% more time on value-added activities compared to what they achieved a decade ago. By automating transactional activities – such as procure to pay, order to cash, record to report, intercompany reconciliation, and even client onboarding – it becomes easier to establish new operating models where finance executives can adjust their workflows dynamically to address the most pressing issues faced by businesses.
To reach their next milestones for finance efficiency in their organizations, CFOs can now shift gears to gain instant insights from automation, minimize human biases, and drive speed in decision-making. They can use AI and RPA-based analysis to optimize financial planning & analysis, capital structures, internal audits, and risk management. Finance transformation with automation will help them become guardians of enterprise value creation and ensure that reports are generated not just for a quarter or month but in real time to guide operations and decisions.