Blockchain technology has emerged as a potential game-changer for various industries, and the financial sector is no exception. Specifically, blockchain holds immense promise for revolutionizing B2B cross-border transactions. But will it live up to the hype, or is it merely a passing fad? This article explores the potential and limitations of blockchain in B2B transactions, separating the sound and fury from its true significance.
The Current State of B2B Payments
Traditional B2B payments are plagued by inefficiencies, particularly cross-border transactions. They are often slow, requiring multiple intermediaries such as correspondent banks and clearing houses, and can take days or even weeks to complete. Additionally, they can be expensive due to the high transaction fees charged by these financial institutions. According to The ECB Blog, the fees for international payments averaged 1.5% for corporates and as much as 6.3% for remittances as of October 2023. These inefficiencies can significantly hinder global trade and commerce, impacting businesses of all sizes.
How Blockchain Payments Work
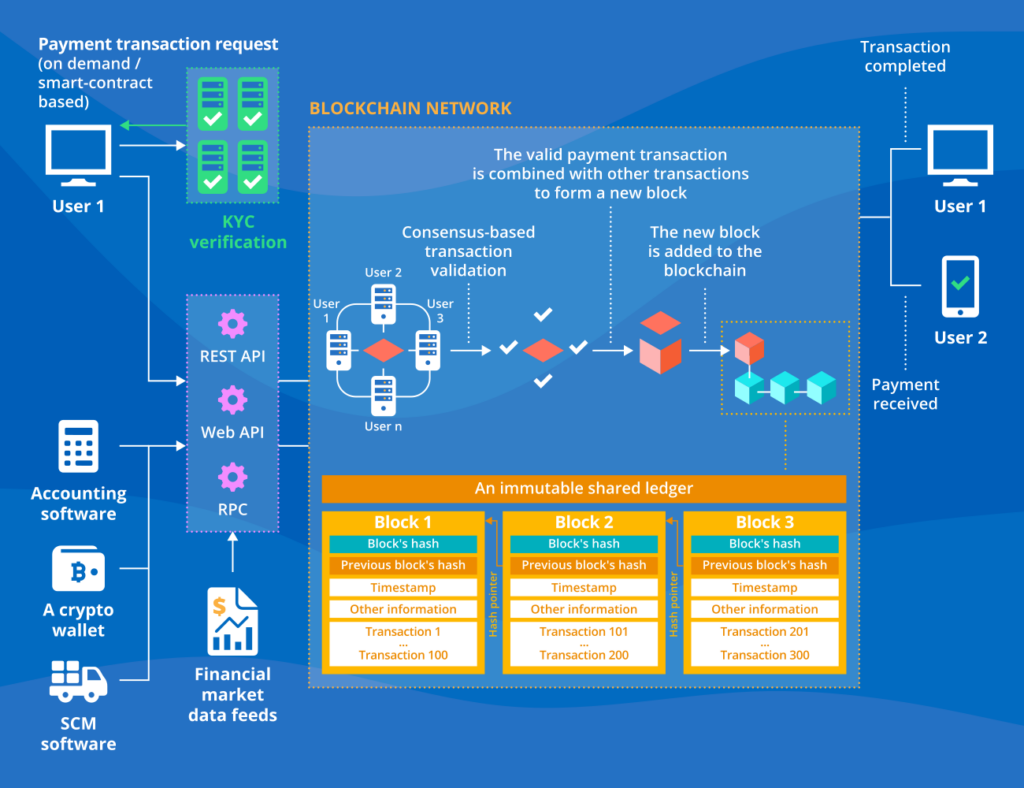
In a blockchain network, participants initiate payment transactions, or smart contracts can execute them automatically based on predetermined conditions. These transactions are broadcast across a peer-to-peer network of nodes that verify them using a predefined consensus mechanism. Once validated, the data is encrypted with a unique code (hash function) and stored in chronological blocks along with timestamps. These blocks form a shared, tamper-proof record known as a distributed ledger, which acts as a single source of truth for tracking payment activity and user identities. All participants maintain their own up-to-date copies of this ledger, ensuring automatic updates whenever new data is added.
Do’s and Don’ts of ERP Implementation: A Client Perspective
Users interact with the blockchain through dedicated web or mobile applications designed for their specific roles (e.g., individuals, businesses, financial institutions). The blockchain solution can integrate with various tools and systems, including crypto wallets, accounting software, financial data platforms, e-commerce platforms, and supply chain management software, depending on the specific use case.
Blockchain for B2B Payments: Primary Use Cases
Blockchain technology offers a unique set of capabilities that can significantly improve the efficiency and security of B2B transactions. Here are some of the primary use cases for blockchain in B2B payments:
- Domestic Payments: Streamlining domestic payments across various industries. Blockchain can facilitate fast and convenient peer-to-peer transactions for retail, healthcare, public transportation, entertainment, hospitality, and more. This can include innovative solutions like QR code-based payments for in-person purchases, eliminating the need for cash or cards.
- Cross-Border Payments: Revolutionizing international trade. Blockchain can enable fast, cost-effective cross-border payments by removing the need for intermediaries like banks or government agencies. This reduces transaction fees and processing times, while also providing end-to-end visibility into all payment data for enhanced transparency and improved control over financial operations.
- Trade Finance: Enhancing security and trust in trade agreements. Blockchain can create tamper-proof records and ensure complete traceability of financial obligations among trading partners. Additionally, smart contracts can automate payment enforcement based on predefined events, guaranteeing timely fulfillment of multi-party agreements and minimizing the risk of payment delays.
The Role of AI in F&A Operations
How Blockchain Can Revolutionize B2B Payments
Blockchain technology offers a unique solution to the challenges of B2B payments. Here’s how:
- Faster Transactions: Blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries, streamlining the transaction process – sorely needed in cross-border transactions. Transactions are submitted by network members or automatically enforced by smart contracts upon predefined events. These smart contracts are essentially digital agreements that can automate specific actions when certain conditions are met. Once a transaction is validated by the network, it is added to a tamper-proof public ledger, significantly reducing processing times, and potentially bringing transactions down to minutes or even seconds.
- Reduced Costs: By removing intermediaries and their associated fees, blockchain can significantly reduce transaction fees. Juniper Research estimates that the total value of B2B cross-border payments on blockchain will exceed $4.4 trillion in 2024, accounting for 11% of the total B2B international payments. The ability to provide cost-effective processing will be a major driver of this growth. This can lead to substantial cost savings for businesses engaged in international trade, freeing up capital for investment and growth.
- Enhanced Transparency: All transactions on a blockchain network are recorded on a shared, tamper-proof ledger, providing complete transparency for all parties involved. This immutable ledger ensures that data cannot be altered or deleted, creating a verifiable and auditable record of every transaction. This can increase trust and accountability in B2B transactions, reducing the need for reconciliation and disputes.
- Improved Security: Blockchain utilizes robust cryptography to secure transactions, making them highly resistant to fraud and cyberattacks. Every transaction is encrypted with a unique hash function, and any attempt to tamper with the data would be immediately detectable. Additionally, blockchain networks are typically permissioned, meaning that only authorized participants can join the network, further enhancing security.
Data Analytics in 2024: 5 Key Trends Every Business Should Know
Limitations and Challenges of Blockchain for B2B Payments
While blockchain offers a compelling vision for the future of B2B payments, there are still challenges to overcome:
- Scalability: Current blockchain networks can struggle to handle the high volume of transactions typical of global trade. For instance, Bitcoin, a popular blockchain network, can only process around seven transactions per second. This is a far cry from the thousands of transactions per second that traditional payment networks can handle. Scalability improvements are necessary for widespread adoption in B2B commerce.
- Regulation: The regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain is still evolving. Governments and financial institutions need to establish clear regulations to ensure the secure and compliant use of blockchain for B2B transactions. These regulations should address issues such as anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) requirements.
- Integration: Integrating blockchain technology with existing financial systems can be complex and expensive. Businesses need to invest in the necessary infrastructure and expertise to leverage blockchain effectively. This may include developing new applications or integrating with existing blockchain platforms.
Accelerating Business with New-Age Technologies
The Road Ahead for Blockchain in B2B Payments
Despite the challenges, blockchain holds immense potential to transform B2B cross-border payments. As scalability improves, regulations are clarified, and integration becomes more seamless, we can expect to see wider adoption of this technology. Early adopters are already realizing the benefits of blockchain. A 2022 PYMNTS survey reported that 37% of businesses already used blockchain for B2B cross-border transactions.
In conclusion, blockchain is not merely sound and fury. It signifies a significant development with the potential to disrupt traditional B2B payment methods. While there are hurdles to overcome, businesses that embrace blockchain early can gain a competitive edge in the global marketplace. By streamlining processes, reducing costs, and enhancing security, blockchain can pave the way for a more efficient and prosperous future for international trade.